Driven by the increasing importance of the Internet of Things (IoT) and ever-more demanding requirements from various industries including heavy vehicles, computer-aided design (CAD) modeling and simulation software are benefiting from not only new features but also greater integration with other software tools.
Powerful software tools are enabling a more multi-disciplined approach to designing vehicles and other systems. The existence of the cloud is allowing data to be easily shared among designers regardless of location, and is serving as a repository to store information for future designs. There is also increasing integration between tools from different companies that is helping to streamline design workflows.
These developments are important as heavy-duty and off-road vehicles continue to grow in complexity, using sophisticated electronics and moving to hybrid and electric drivetrains. At the same time, designers face the pressure to shorten design and development cycles, thus requiring software that can navigate through the complexities of these cycles.
“There is a continual drive to shorten the design and development of a vehicle and its powertrain, whilst also delivering ever-challenging powertrain performance targets and exploring alternative powertrain options,” says David Bell, Commercialization Manager of Ricardo Software.
“There is an increasing need for system-level analysis, using products such as Ricardo’s Modelica-based Ignite, to find optimum hybrid and electric powertrain solutions early in a design program,” adds Felipe Brandao, Vice-President Product Management, Ricardo Software. “Such tools can be used to optimize the thermal management of the vehicle, coupled to higher-fidelity CFD (computational fluid dynamics) and FEA (finite element analysis) tools, to model components such as a battery pack.”
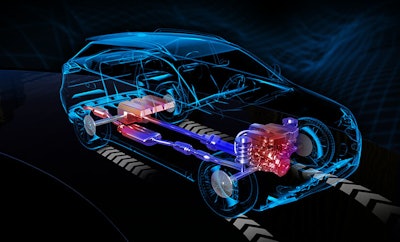 Figure 1: Ricardo’s Modelica-based Ignite provides a means to optimize hybrid and electric powertrain solutions early in a design program.Ricardo Software
Figure 1: Ricardo’s Modelica-based Ignite provides a means to optimize hybrid and electric powertrain solutions early in a design program.Ricardo Software
READ MORE: Ricardo Software 2020.2 Includes Battery Modeling Capabilities
Simulating the operating environment
An increasingly important consideration in developing heavy-duty and off-road vehicles is simulating how a product or system will look and behave from physical, electrical, and other factors. Simulation software is particularly important in ensuring the comfort and safety of the operator. The ability to accurately simulate the operator’s environment is of utmost importance, says Steve Vickers, Product Manager NX Automotive, Transportation and Heavy Equipment at Siemens Digital Industries Software.
“We need to work out how the operator is sitting inside the vehicle cabin. Ergonomics—the position of the operator’s elbows, the steering wheel, the location of the head, where the mirrors will be placed—need to be carefully simulated.”
Carefully modeling the vehicle operating environment is important, but so is the ability of the vehicle’s electrical and mechanical systems to work together properly. With many simulation tools part of software suites integrating design, viewing all aspects of a vehicle’s internal systems is far easier.
Siemens’ NX software (Figure 2) is an integrated toolset addressing design, simulation, and manufacturing. The tool suite addresses product modeling, cable and wiring routing, simulation, and workflow.
“For instance, when the electrical engineer defines which components are used, the connection information appears so that the mechanical engineers can see where cabling is routed,” says Vickers, using the example of a vehicle’s engine. “Once the mechanical engineer simulates the cable routing, the electrical designer in turn can see the effects on electrical performance.”
CM Labs recently released Vortex Studio 2019b, a major version update to Vortex Studio. According to the company, the latest version makes it easier for users to install, build, test, and deploy real-time simulation.
One feature of particular interest to the heavy vehicle industry is an expanded Deformable Terrain zone with features that go beyond digging and pushing soil. While still allowing the deformation of a given surface using digging tools (bucket or blade), vehicles' wheels can now directly impact the terrain, compressing and deforming it on each pass, creating ruts and graphical marks modeled on specific textures.
Another feature of Vortex Studio is parallax occlusion mapping, where materials can have a pronounced depth 'look' while still being a 2D element. A self-shadowing capability enables materials with a height map to render a dynamic shadow, adding depth and environmental realism.
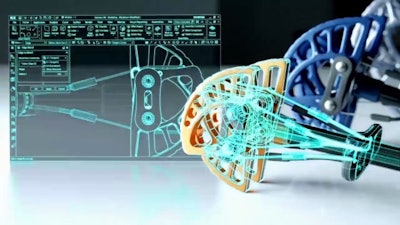 Figure 2: Siemens PLM’s NX software gives designers a complete suite of design tools addressing modeling, simulation, manufacturing, and workflow.Siemens PLM
Figure 2: Siemens PLM’s NX software gives designers a complete suite of design tools addressing modeling, simulation, manufacturing, and workflow.Siemens PLM
The power of IoT
In an age when use of IoT is increasing, the data generated by today’s software tools can build up a rich repository of information for future design, as well as provide historical data for tasks such as predictive maintenance.
Citing an example of a crane manufacturer, Paul Brown, Senior Marketing Director at Siemens PLM Software notes, “The crane manufacturer is using a lot of sensors, so we can feed this information to the design team so they can make informed decisions going forward. If you start seeing historical data that there are certain conditions that need to be looked at, the designer can then solve problems during design.”
Virtual reality and artificial intelligence are also starting to make their mark in simulation and modeling. Siemens’ NX software integrates Virtual Reality into the desktop application and is accessible with one click, extending familiar interactions into a truly immersive 3D environment. This enables users of various disciplines to more easily collaborate during product development.
“While virtual reality has been around awhile, it has been limited to big companies because of cost and complexity. Now you can buy lower cost hardware which gives designers the powerful capability of being able to virtually sit in the cockpit and define and refine features.”
Siemens NX offers an expert personal assistant that uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to track and learn from user actions. It then predicts the NX commands the user will likely use next based on the context of what they are currently doing and then presents those commands on a compact adaptive UI panel.
Leveraging the cloud
Software vendors are also using the power of the cloud to market tool suites promoting collaborative design and development. Dassault Systemes has enhanced its Catia V5 software (Figure 3) with its 3D Generative Innovator, a cloud-based generative modeling environment that combines graphical visual scripting and interactive 3D modeling, with the ability to use one or the other interchangeably at any time.
“More customers are asking for CAD that is accessible anytime, anywhere and on any device--in other words cloud based,” says Craig Therrien, 3DEXPERIENCE WORKS Senior Portfolio Manager for Dassault Systemes. “Think of Netflix, Prime Video and other online services. You can access them on several devices – phone, PC, tablet, TV. Our customers see this as an advantage.”
Cloud-based software also does away with concerns about having to download the latest updates. “And the fact that they are always accessing the latest version of CAD means no more worries about upgrading and which version of CAD their customers and/or vendors are running – everyone can run the same version,” notes Therrien.
The software has a Function Driven Generative Designer which allows designers to automatically generate optimized conceptual parts and assemblies from functional specifications. The designer simply provides a set of requirements, including the 3D envelope, connections, the loading scenario, material, weight reduction targets for lightweight engineering, and the desired manufacturing process, either traditional, such as milling, casting or forging, or additive manufacturing. The push of a button runs a simulation process and generates the optimized concept assembly shapes.
 Figure 3: Dassault Systemes’ Catia V5 software provides a cloud-based generative modeling environment that combines graphical visual scripting and interactive 3D modeling.Dassault Systemes
Figure 3: Dassault Systemes’ Catia V5 software provides a cloud-based generative modeling environment that combines graphical visual scripting and interactive 3D modeling.Dassault Systemes
Drag and drop
Designing software for easier use is also a priority for software vendors. For instance, IronCAD says its INOVATE CAD software has a drag-and-drop environment to speed design and enable more users to access the tools. The tools make 3D models and engineering project data available to marketing, sales, and training teams so they can work together and communicate more effectively.
Other tool vendors have modified the underlying algorithms of their software tools to make it easier for users to model parts. For instance, RS Components (RS) has unveiled the latest version of DesignSpark Mechanical, its free 3D CAD modeling software. Developed in conjunction with Ansys Inc., the tools use direct modeling technology rather than the parametric methods used by traditional CAD software, enabling users to rapidly prototype or reverse engineer any physical object.
Key features include an equations tool to sketch complex curves, constraint-based sketching and a dedicated 3D sketch mode, custom rendering, enhanced shading, and a fly-through camera mode. DesignSpark Mechanical also offers access to a 3D catalog of tens of thousands of 3D models from leading component manufacturers.
3D sculpting is also catching on as an alternative modeling technology to parametric methods. According to Therrien, “We’re hearing a lot of excitement around our subdivision modeling capabilities currently. This is relatively new for our core user base, and we see a lot of users diving into the world of 3D sculpting. And it’s not just artists and industrial designers – mechanical engineers are trying it out. It’s amazing how quickly and easily you can create incredible shapes that would take hours or even days to produce using traditional parametric modeling techniques.”
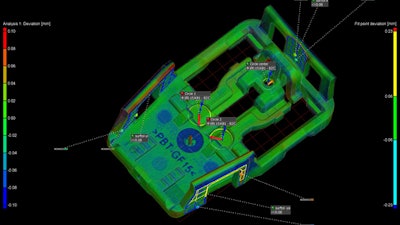 Figure 4: Volume Graphics VGSTUDIO MAX version 3.4 software provides a visual, comprehensive, and easily understandable representation of a part’s geometrical deviations and tolerances.
Figure 4: Volume Graphics VGSTUDIO MAX version 3.4 software provides a visual, comprehensive, and easily understandable representation of a part’s geometrical deviations and tolerances.
Where no CAD files exist
Software vendors are also trying to address design scenarios with legacy parts, where CAD may not be available. Volume Graphics has released its VGSTUDIO MAX version 3.4 software (Figure 4), which has added features to help designers and manufacturers capture and interrogate product data to improve final quality.
The program’s Reverse Engineering Module can generate surfaces from a CT scan, or from any voxel model converted from a closed mesh/point cloud scan, using an auto-surface function. The feature enables manually generated design models to be available digitally—without the need for a CAD designer or reverse-engineering specialist.
The software makes it possible to generate and archive 3D CAD models of legacy parts, as well as update those models in which the actual part or tool deviates from the master CAD model. This automates the creation of digital twins of individual parts and helps to validate the model-to-part relationship. The program enables the recreated or newly validated CAD model to be exported as a STEP file to any CAD system.
These capabilities are particularly useful, given that more companies want to document part data and use it in future designs.