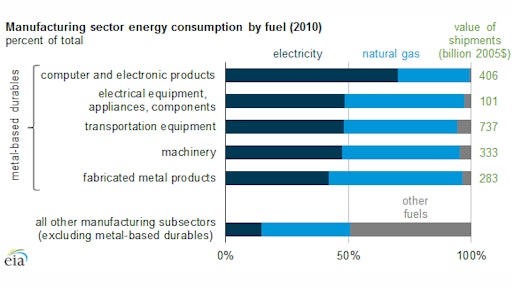
Unlike many manufacturing industries, the energy used for the production of metal-based durables (MBD) is mostly electricity and natural gas, rather than other fossil fuels (residual fuel oil, diesel, liquefied petroleum gases, natural gas liquids and coal) or renewable sources. MBD producers are therefore well-positioned to benefit from energy efficiency programs and the increased availability and lower cost of natural gas.
MBD industries comprise fabricated metal products, transportation equipment, machinery, computers and electronic products, and electrical equipment appliances and components. Cutlery, aircraft engines, photocopiers, computer hard drives, and electric motors are some examples of the many products produced in the MBD industries.
Many other industries are more energy intensive than MBD industries, including petroleum and coal products, paper, primary metals and chemicals. MBD industries used 942 trillion British thermal units (Btu) of energy in 2010, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) Manufacturing Energy Consumption Survey (MECS) 2010. This represents 7% of total manufacturing energy use.
MBD industries used 466 trillion Btu of electricity in 2010, representing nearly 20% of total electricity use in manufacturing. Electricity accounted for nearly 50% of total energy used by MBD industries. Some other industries where electricity use accounts for 40% or more of their energy use include textile mills, apparel and aluminum production.
MBD manufacturing is typically housed in a building, and the manufacturing processes are not as energy intensive as many other industries. Direct non-process electricity use, which includes facility heating, ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC), facility lighting and other facility support, represents 36% of MBD electricity use as compared to 14% of electricity use in other manufacturing. As a result, buildings are a particularly important part of efforts to reduce energy use in the MBD industries.
EIA's Annual Energy Outlook 2014 (AEO2014) projects that shipments for MBD industries will increase substantially from 2012 to 2040. MBD industries will benefit from the increased availability and lower cost of natural gas. These industries are expected to continue to have high levels of innovation that contribute to growth, particularly in the computers and electronic products and transportation equipment industries. MBD industries are also expected to continue to improve their international competitiveness. Given the high dependence of MBD industries on electricity, there are significant potential benefits from improved energy efficiency associated with machine drives, buildings and the reduction of losses associated with on-site electrical distribution systems.