For ADAS testing, Vector’s measurement and calibration tool CANape now supports the inertial system ADMA from GeneSys. This will enable users by way of the Ethernet interface to record all ADMA measurement data of several networked vehicles and set it off one to the other – completely synchronously and in real-time. The GNSS-aided inertial system ADMA from GeneSys is used worldwide as a reference system in testing Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and automated driving functions.
The implementation of the ADMA driver in CANape version 16.0 Service Pack 5 or higher, enables users to record the synchronous ADMA measurement data of several vehicles in CANape via Ethernet/WLAN.  GNSS aided inertial system ADMA with an output rate of 1,000 Hz.
GNSS aided inertial system ADMA with an output rate of 1,000 Hz.
Thanks to the GNSS-aided inertial system ADMA all states of movement, such as acceleration, speed, position, turning rate, position and side slip of the moving vehicle, are recordable to a high degree of precision. Moreover, the ADMA DELTA function permits centimeter-precision measurements between several vehicles, such as distance, relative speed and relative angle - done in rea-time and only via wireless connection between two ADMAs. No additional hardware is needed. Calculation is done directly in the ADMA. This makes the validation and tests of all types of distance sensors (e.g. Radar or LIDAR) and driver assistance systems (e.g. Adaptive Cruise Control ACC, Forward Collision Warning FCW and Autonomous Emergency Braking AEB) easier and more reliable.
Application fields
CANape records measurement data from many common high-resolution radar, video and LIDAR sensor components, such as IBEO HAD, Quanergy, Velodyne or µEye cameras as well as others with a DirectX driver. Thanks to the Vector-implemented ADMA driver, the GNSS-aided inertial system from GeneSys can now be used as a reference system - representative for all high-precision inertial measuring units specially deployed for ADAS development and autonomous driving.
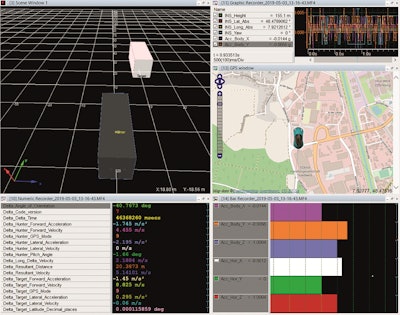
 Recording fully synchronous ADMA measurement data with CANape via WLAN connection of several ADMAs.
Recording fully synchronous ADMA measurement data with CANape via WLAN connection of several ADMAs.
Synchronization – online and offline
The measurement data of the GNSS-aided inertial system ADMA is based on the GPS time. The same time master allows all ADMAs to be synchronized with each other. There are two possibilities: online in real time or offline for measurement data evaluation. Real-time synchronization is possible, for instance, even during the test run by way of using a WLAN connection between the vehicles used in the test. Benefit: the ADMA data is evaluated in real time simultaneously to the data being recorded. Offline synchronization allows measurement data from non-networked vehicles to be brought together using the GPS time-stamp.
Along with evaluation of advanced driver assistance systems, such as ACC, FCW, AEB and LDW, the ADMA reference system is also first choice when it comes to driving dynamic analyses and autonomous driving. It meets the requirements exacted by the international test standards.