
With the rapid development of electric vehicles and renewable energy, battery technology is reaching a new milestone – solid-state batteries. Within this field, battery equipment suppliers are facing unprecedented opportunities and challenges. Seizing opportunities and meeting market demand for efficient, reliable, and innovative battery production equipment will be crucial in determining the future market leaders.
In the upcoming “Li-ion Battery and Manufacturing Equipment 2024” report by Interact Analysis, the market landscape of current Li-ion battery equipment suppliers is analyzed from multiple perspectives. This article will discuss the impact of solid-state batteries on Li-ion battery manufacturing equipment and the challenges faced by traditional Li-ion battery equipment companies. It will also share new developments from equipment manufacturers in the solid-state battery field.
Differences in production processes between solid-state and liquid-state batteries
The production process of solid-state batteries is significantly different from that of traditional liquid electrolyte batteries. In the manufacturing of solid-state batteries, solid electrolyte materials are first prepared through powder metallurgy or chemical synthesis methods. Then, the active materials of the positive and negative electrodes are stacked with the solid electrolyte layer and pressed and sintered at high temperatures to form the electrode sheet. The diagram below illustrates the differences between the manufacturing processes of traditional liquid batteries and solid-state batteries (using sulfide-based solid-state batteries as an example).
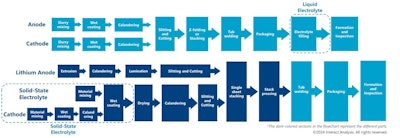 A comparison of the manufacturing processes of traditional liquid and solid-state batteries.Courtesy: Interact Analysis
A comparison of the manufacturing processes of traditional liquid and solid-state batteries.Courtesy: Interact Analysis
However, the manufacturing technology and equipment requirements for solid-state batteries also present new challenges for traditional battery equipment manufacturers. Although semi-solid and quasi-solid batteries may dominate the market in the short-term, the future application of fully solid electrolytes and the use of metal Li-ion as an anode material will inevitably lead to major reforms in production processes. Therefore, equipment manufacturers must transition accordingly in advance.
For instance, some manufacturers have begun experimenting with dry electrode technology in the front-end process. For example, Yinhe has developed its second-generation, dry electrode, mass production equipment, while PNT has signed an order with Tesla to supply dry electrode process equipment. The concept of dry electrode technology is like that of solid-state batteries, as it abandons traditional liquid solvents while adapting to current process flows. Through such technological upgrades, manufacturers can gradually adapt to new process requirements without significantly altering back-end equipment, thereby maximizing economic benefits.
Three advantages of dry electrode technology
Dry electrode technology is a solvent-free production method that forms sheet or film electrodes by directly mixing positive and negative electrode materials with binders and then rolling, spraying, or extruding. Compared with wet processes, dry processes have the following advantages in manufacturing solid-state batteries:
- Lower production costs and reduced environmental impact: It eliminates the steps of slurry mixing, drying, and solvent recovery, reducing production costs and minimizing environmental impact.
- Higher energy density and durability: The contact between the active material and the conductive agent is tighter, enhancing the battery’s energy density and durability.
- Wide range of applications: For example, Li-ion metal anodes can only be made using the dry process.
Market dynamics and industry outlook
Interact Analysis also compiled a list of new developments from major Li-ion battery equipment manufacturers in the solid-state battery field. Significant breakthroughs in the solid-state battery field are mainly driven by established liquid Li-ion battery manufacturers. These companies leverage their deep industry experience and strong R&D capabilities to maintain a lead in technological innovation. Given the high technical barriers and significant capital requirements in this industry, we are cautious about the likelihood of new entrants making significant progress in the short term.



















